What does XRechnung mean?
Conversion of an EU standard into the national standard XRechnung
XRechnung – In Germany, it is estimated that more than 30 billion invoices are sent by post every year. The origin of the XRechnung is the european Commission’s efforts to promote e-procurement.
2014 Kick-off for the development of electronic bill
XRechnung is the official standard for electronic invoicing in German administrations. It was developed in accordance with Directive 2014/55/EU of the European Union. KoSIT, (Coordination Office for IT Standards) manages the XRechnung standard for the IT Planning Council. It also works with experts from various levels of government to improve and update XRechnung .
Table of Contents
Directive 2014/55/EU on e-invoicing in public procurement was already adopted in 2014. The aim is to make all contracting authorities obliged to accept and process invoices electronically only by way of pan-European procurement procedures. The idea is that the transition to electronic invoices, which can be processed automatically, can save significant costs on the part of the public administration.
2017 Publication of the standard
The European standard for electronic invoicing, known as EN16931, was prepared by a committee called CEN/TC 434 within the European standardization organization CEN. In March 2017, member states agreed on the first two parts of this standard. This was an important step that had to be taken before they could complete the national standard XRechnung .
From 2020, XRechnung
From the end of November 2020, the XRechnung will be mandatory for all contractors of contracting authorities. Since that time, billers have been obliged to submit invoices electronically to the federal government in the XRechnung standard.
What exactly is the XRechnung? When is this invoice format mandatory? How can XRechnung be created and what is the difference to ZUGFeRD? The answers to these questions, what to consider and how you can make the changeover, can be found here.
Electronic invoice formats and standards
- Unstructured data formats: Invoicing in .pdf-, .jpg or .tif format
- Structured data formats: XML, EDI, XRechnung
- Hybrid data formats: PDF/A, ZUGFeRD
- Transmission channels: e-mail, DE-mail, e-mail or web download
The XRechnung
Standard in Germany for contracting authorities
In Germany, there is a special form of electronic invoicing, the XRechnung. This is the standard method for sending invoices for government contracts electronically. The government requires companies that do business with it to use XRechnung . This is a legal requirement. XRechnung is considered the official German standard for this purpose and complies with European data model standards.
The idea behind this is not only to make official transactions more efficient, but also to encourage companies to use electronic invoices in business transactions with each other (B2B sector). In order for all this to work within the framework of the law, the invoices must be in XML format and can also use a hybrid format, the so-called ZUGFeRD.
Put simply, XRechnung is the way electronic invoices for public procurement are sent in Germany, and it also pushes companies to use electronic invoices in business transactions with each other. It helps streamline processes and ensures compliance with laws.
XRechnung mandatory from 2020
From 27 November 2020, all contractors who supply goods or services to the federal government will be required to issue e-invoices in the structured formats of XRechnung . This means that public contractors in Germany can now send more electronic invoices (XRechnung) to the federal authorities. Other types of invoicing are no longer allowed. Only these invoices will be accepted in the future.
The obligation to prepare and submit XRechnungen from 27 November 2020 is the result of the requirements of the EU Directive 2014/55/EU and the E-Accounting Regulation, which the Confederation has adopted in the implementation of EU rules. With the exception of a few exceptions, such as the small limit and special security arrangements, this obligation applies without restriction. Conversely, contracting authorities must accept these XRechnungen from certain reference dates. This has been the case for the highest federal authorities and constitutional bodies of the federal government since 27 November 2018. All other institutions that are recipients of the invoice within the meaning of the Federal E-Rech-VO shall observe 27 November 2019 as the cut-off date. In the period up to 2020, the contracting authorities of the Länder and municipal clients will also follow.
What do XRechnungen look like? What is the XRechnung format?
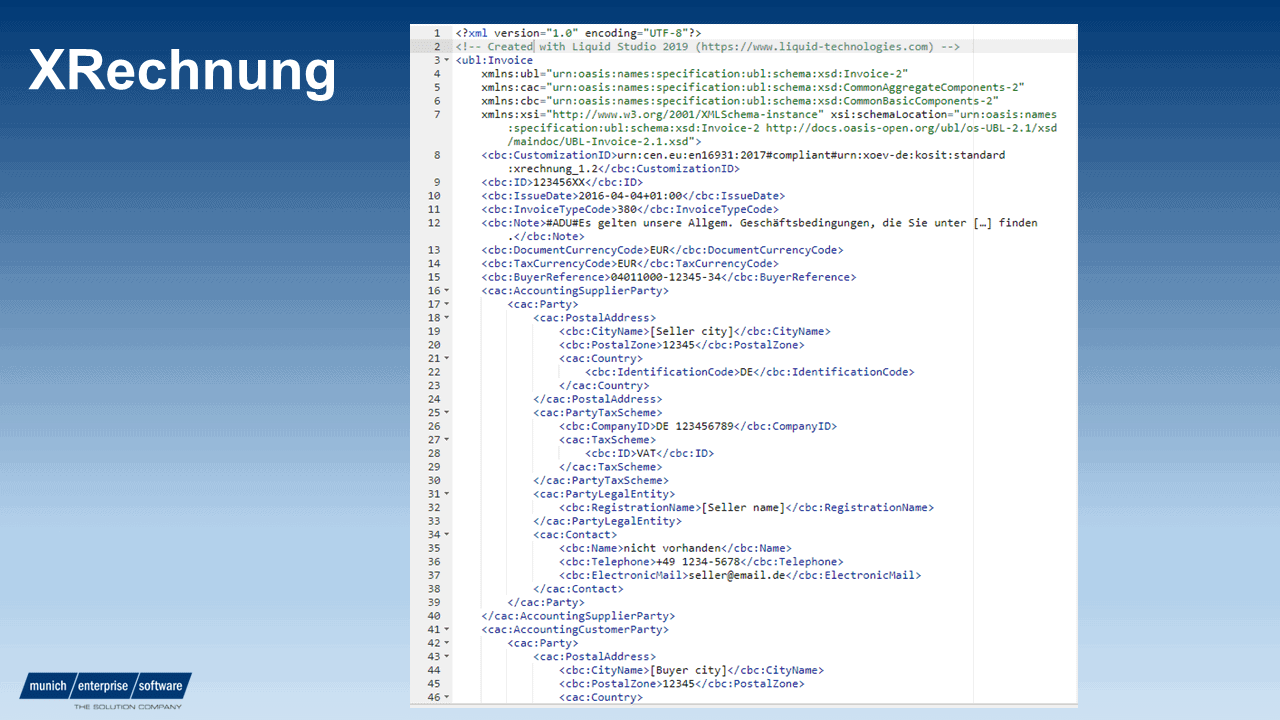
From the user’s point of view, an XRechnung is a data exchange model that provides all data of the invoice in a structured manner as an XML format. It is a semantic data model that maps all legally binding contents of an invoice and serves machine processing. This means that XRechnung contain all general mandatory information of an invoice in accordance with Section 14 UStG and all special components of an e-invoice in accordance with Section 5 E-Rech-VO.
This German data exchange standard can be implemented as a technology-neutral format in IT solutions and is purely machine-readable. From July 1, 2019 to December 30, 2019, version 1.2.0 of XInvoice is valid. As of January 1, 2020, the new version 1.2.1 must be used for XRechnungen.
Who needs to create an XRechnung ?
An XRechnung is a standardized electronic invoice format in Germany that is used in accordance with the electronic invoice exchange between companies and public administration. The obligation to create an XRechnung depends on the business partner. Companies that provide services to the public administration are usually obliged to issue XRechnung. This applies to companies that provide supplies or services to federal, state and local authorities.
What is the routing ID?
The routing ID is used to forward incoming e-invoices to the corresponding invoice approval systems within certain administrative units. To ensure that a XRechnung reaches the correct invoice recipient, the recipient must have their routing ID and include it in the e-invoice. This routing ID should have been specified either during the mapping process or at the time of ordering.
Structure of the ID
The structure of a routing ID consists of the following components:
- State code: This is a code that indicates the specific state or region within the country where the administrative unit is located. It serves as the first part of the routing ID.
- Administrative district code: The administrative district is a subdivision within the state or region. The measure of the administrative district is used to further narrow down the goal. It stands immediately after the country code.
- County code: Within the administrative district, there may be counties or other subdivisions. The county code identifies the respective county within the administrative district. It follows the key figure of the administrative district.
- Municipal Code: Municipalities are local government units, and the municipal code indicates the exact municipality within the county. This component follows the circle code.
- Delimiter “-” (hyphen): This hyphen serves as a separator to distinguish between the fixed part of the routing ID and the variable manager number that follows it.
- Fine-tuning: Fine-tuning refers to additional information that might be required to accurately locate the target within the specified municipality or administrative unit. It comes after the hyphen separator.
- Delimiter “-” (hyphen): Another hyphen is used to signal the end of the variable manager number section and prepare the last component.
- Check digit: The check digit is calculated based on the values in the previous fields (state code, code, district code, municipality code, fine addressing). It is used to verify the correctness and integrity of the routing ID.
Adherence to this structure is essential to ensure the correct routing of electronic invoices to their destinations.
How does the transmission of the XRechnung take place?
There are different ways to transfer the XRechnung.
Central invoice receipt platform of the federal government (Leitweg-ID with “991” or “99000000”). The website of the Confederation’s central invoicing platform offers you the opportunity to create an electronic invoice via a web form, to submit a created electronic invoice or to view the processing status of the electronic invoice you have submitted. Website: https://xrechnung.bund.de/prod/authenticate.do
Further transmission paths:
- E-mail transmission: XRechnung can be sent by e-mail.
- Online portals: Depending on the customer, different online portals can make it easier to upload and submit XRechnung .
- Transmission by DE e-mail: DE e-mail can also be used as a method of transmitting XRechnung .
- Transmission via the Peppol network: XRechnung can be sent via the Peppol network.
These different delivery options provide flexibility for sending XRechnung, depending on your preferences and the recipient’s requirements.
What are the requirements for archiving?
The requirements for archiving electronic invoices are regulated differently in the countries. Since there are no uniform rules for archiving, the respective national standards must be checked.
SAP XRechnung Example
Differences between ZUGFeRD 1.0 and ZUGFeRD 2.0
The following changes are to be observed in the ZUGFeRD 2.0 specification with regard to version 1.0:
- Design principles of EN 16931-1
- Deviations in profiles
- Rules
- Calculation method
- Other tags in syntax mapping
- Code lists
- Embedding in PDF/A-3
Software for XRechnungen
Companies supplying goods or services to contracting authorities were obliged to introduce XRechnung, a special electronic invoicing format, by 27 November 2020. To meet this requirement, they had to prepare and switch to software solutions that could process XRechnung.
This change required technical adjustments and changes to the internal invoicing processes. Importantly, this obligation applies to companies of all sizes.
Not only the suppliers, but also the software providers responsible for invoicing solutions had to develop software that is compatible with XRechnung . These software vendors have developed conversion tools to convert normal invoices to XRechnung format.
Many companies that use ERP systems such as SAP, Microsoft or Oracle needed these solutions because their systems have standardized interfaces for importing and exporting data. These interfaces formed the basis for the conversion of invoices into the XRechnung format. In addition, the reverse conversion process, i.e. the conversion of XRechnung invoices back into standard formats, was also possible.
Accounting and ERP software vendors develop specialized application solutions that allow companies to create and process ZUGFeRD invoices as part of traditional software. It is also possible to implement ZUGFeRD in company-specific software solutions. Of course, we also have the right add-on for SAP.
Difference XInvoice Standard and ZUGFeRD
Purely machine use or also readable by humans
The main difference between the XInvoice Data Model and ZUGFeRD is that XCalculations are pure XML files for machine processing. In contrast, a ZUGFeRD invoice is also readable by humans. According to this hybrid data model, documents contain a PDF file in addition to the structured electronic file, which can be used by the user.
They can be delivered by e-mail. The invoice recipient receives a PDF document to which the XML file is attached. It can print the invoice as a PDF file and insert it into the system as an XML file. The ZUGFeRD 2.0 version fully complies with the requirements of EU standard 16931 and can therefore also be used for sending invoices to contracting authorities.
Another difference between the XRechnung standard and ZUGFeRD (Central User Guide of the Forum for Electronic Invoicing Germany) lies in the area of application. XRechnungen are the legal invoice format for public administration contracts. Thus, the data model of the XRechnung is mainly used in the B2G area (Business to Government).
In contrast, many companies in the B2B sector prefer the FORMAT ZUGFeRD. ZUGFeRD enables an optimized exchange of invoices between companies and is also suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises that do not have a strong IT structure. Since ZUGFeRD additionally provides the invoice data as an image part in the PDF, companies that do not have automated invoice processing can also receive such invoices.
Conversely, those companies that process invoices largely automatically transfer the invoice data of the XML data to their systems. Due to the hybrid structure (XML and PDF document), all invoice recipients can use ZUGFeRD ideally.






