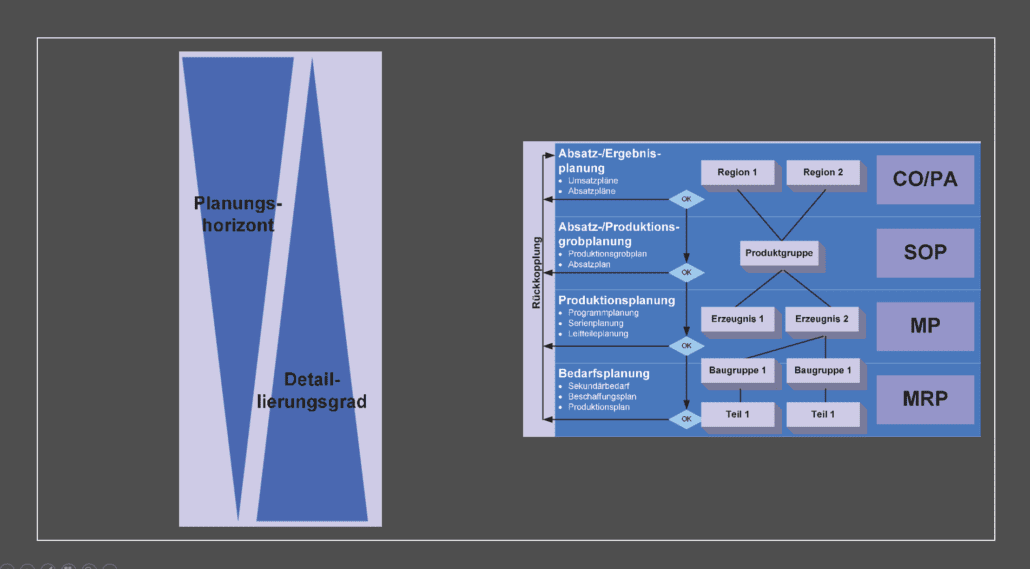
SAP Disposition – Definition and Tasks
SAP Disposition – From our experience, scheduling in SAP ERP is one of the most demanding tasks. At the same time, however, it is often underestimated in practice. This is reflected in a misrepresentation of the position of dispatcher, in insufficient attention during the introduction and in the current operation, up to a lack of further training in this area.
Table of Contents
- SAP Disposition – Definition and Tasks
- Material disposition
- Material requirements planning according to Gabler
- Requirements types in material requirements planning
- Tasks of material requirements planning
- Delimitation of demand planning for programming
- What are the most important transactions for MRP in SAP S/4?
- What are the most important SAP tables for MRP?
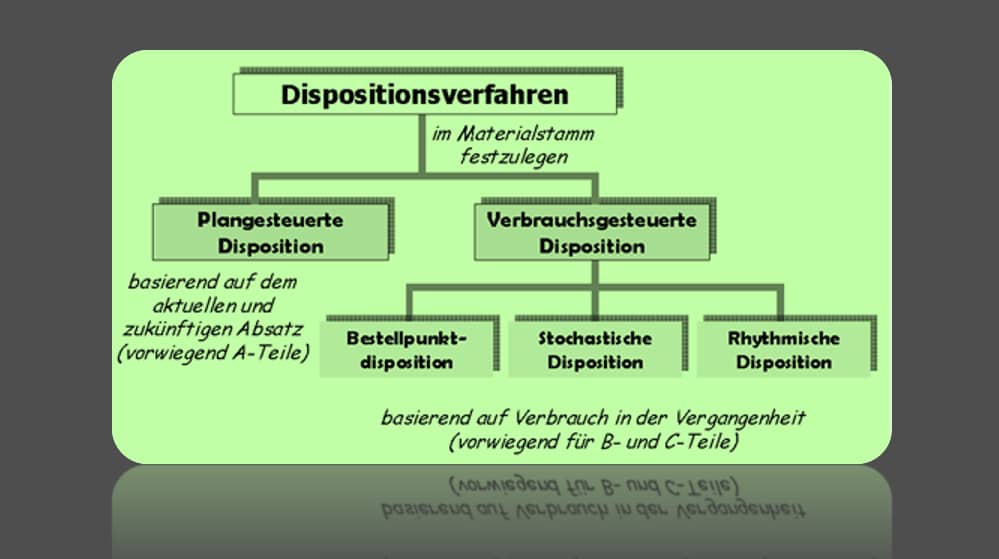
Even experienced SAP consultants regularly reach your limits as part of an introduction and optimization here. Customers like to look for a simple switch or one setting that makes it easy to solve this task. Unfortunately, we have to disappoint you at this point. They will not find a simple solution here.
With this article we would like to give you an introduction to the world of material planning. Every journey, however long, begins with the first step. Learn about the basic terms and basics here. We wish you every success in this.
Material disposition
The main task of material planning is to procure the right material in consistent and prescribed quality, neither too early nor too late in terms of quantity.
The material disposition is intended to
- through material requirements planning and purchase order invoice
- optimal orders and sufficient readiness for delivery
secure.
Material scheduling can refer to individual parts or assemblies.
It includes all the products needed for the manufacture of a product or service, regardless of their final destination within the company: raw materials (including wood, steel, concrete, paper), semi-finished products, parts and assemblies, finished products, assemblies and parts and so on …
Material requirements planning according to Gabler
Definition of Materials Requirement Planning
Material requirements planning is the presentation of the materials required in a planning period according to type, quantity, quality and time structure (secondary, tertiary requirements). The aim of material requirements planning is the realization of a cost-optimal material supply; in the optimum, only as much material is available as is needed at short notice.
Sub-areas of demand planning
Requirements determination: Comparison of gross demand and material inventory shows the procurement requirement (net demand) on material supply planning: Determination of demand dates taking into account the respective demand structure and the conditions on the procurement markets Assortment planning: Substitution planning, make-or-buy decision, limitation of material types
Requirements types in material requirements planning
Gross demand, net demand, primary demand and dependent demand
In DEMAND planning, you distinguish between the requirement types Gross Demand, Net Demand, Primary Demand, and Dependent Demand:
- Gross requirements: The quantity requirements for products, semi-finished products and raw materials resulting from sales orders or forecast orders, without taking into account any existing stocks or quantities already in supply.
- Net demand: Results from the gross demand minus the available stock. The on-hand inventory is the balance from the physical inventory plus purchase order stock minus reservation stock.
- Primary requirements: Primary requirements include all finished products or products from the product range that are required in a planning period. The primary demand, which is made up of the market demand for products and spare parts, is the demand of the highest structural level, which results from a forecast or a concrete customer order.
- Secondary requirements: Secondary requirements include all components and assemblies that are required for the manufacture of the products. These components can either be manufactured in-house or sourced externally (make-or-buy). The secondary demand that is required to cover the primary demand is determined by the BOM resolution.
Tasks of material requirements planning
Tasks of material requirements planning
- the monitoring of stocks
- the preparation of procurement proposals for purchasing and production
- Dissolution of BOMs
Consideration of
- best possible delivery readiness
- Minimizing costs
- Minimization of capital commitment
- Material requirements planning / scheduling = strategic control center for the entire logistics chain in the company
Delimitation of demand planning for programming
The production program is the starting point for material requirements planning.
What are the most important transactions for MRP in SAP S/4?
In SAP S/4HANA, the most important transactions for MRP (MRP) are usually:
MD01 – Individual Requirements Planning: This transaction is used to plan the demand for a single material or material group.
MD02 – Multilevel MRP: Allows you to perform MRP planning for multiple materials in a multi-level production structure.
MD03 – Requirements Listing: This transaction provides an overview of the material requirements and detailed information about the requirements structure.
MD04 – Display of Ongoing Planning: You can use this transaction to display the current status of MRP.
MD05 – Individual Requirements Display: This allows you to display the demand for a single material or group of materials.
MD06 – Individual Requirements Display for Planned Orders: Allows you to display the requirements for planned orders.
MD07 – Planned Order Display: Displays the requirements for planned orders.
MD08 – Updating Planned Orders: You can manually update the planned orders here.
MD09 – Valuation Run for Planned Orders: Allows you to value the planned orders.
MD10 – Mass Change: Enables mass modification of requirements.
These transactions offer various options for planning and managing material requirements in SAP S/4HANA. However, depending on the needs of your business, further transactions may be required.
What are the most important SAP tables for MRP?
MARC – Material Master: This table contains material master data such as material type, storage location data, MRP data, availability check, and much more.
MARD – Storage Location Data for Material: Contains location-level data for materials, including inventory quantities, reserved inventory, planned inventory, and open purchase orders.
MSEG – Document Segment: Contains data on material movements, including receipts, issues, reservations, and inventory adjustments.
RESB – Reservation/Dependent Requirements: Contains data on reservations and dependent requirements for materials.
PLAF – Planned Orders: This table contains planned orders that have been created as part of MRP.
AFKO – Order Header Data PP Orders: Contains header data for production orders that were created as part of MRP.
AFPO – Order Item Data PP Orders: Contains item details for production orders that were created as part of MRP.
RESB – Reservation/Dependent Requirements: Contains data on reservations and dependent requirements for materials.
PLKO – Task List Header Data: Contains header data for BOMs and routing that are used in MRP.
PLPO – Task List Item Data: Contains item details about BOMs and routing used in MRP.